Collisions Detection: DirectSAP
The DirectSAP component belongs to the category of Collision Detection. In this section, we describe the two collision detection methods based on the "Sweep and Prune" algorithm, noted SAP. The SAP method belongs to the topological methods for broad phase, based on the positions of objects in relation to others.
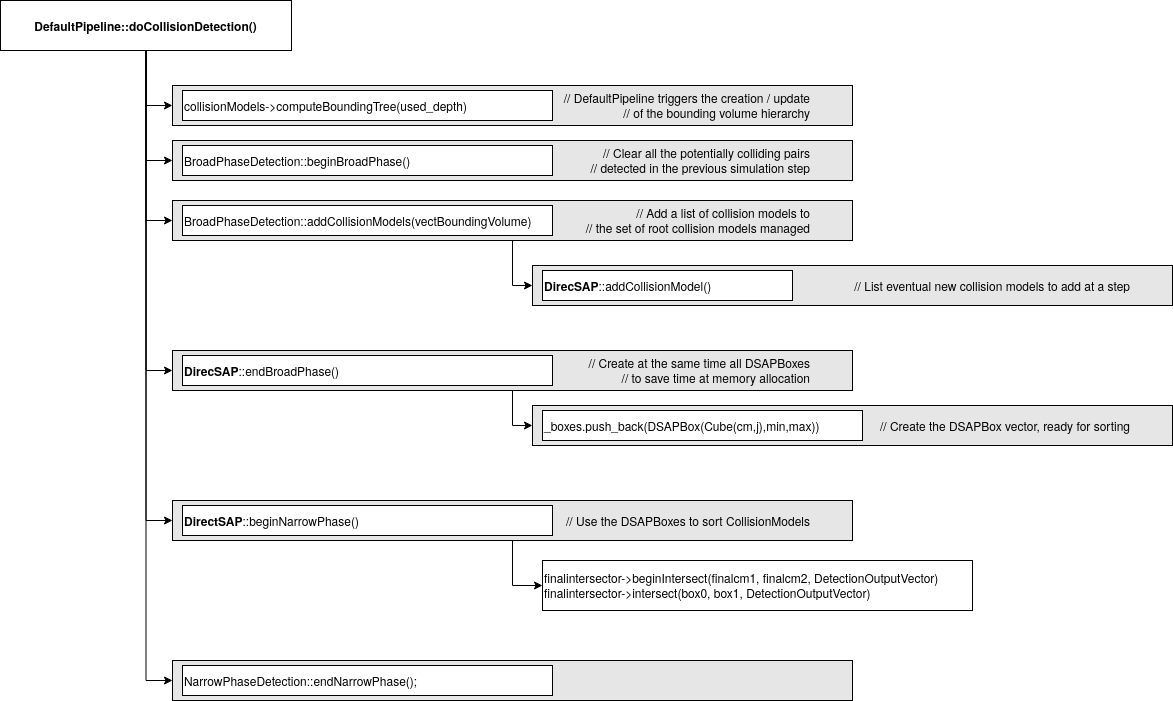
DirectSAP corresponds to the implementation of SAP in its "direct" version, i.e. at each step it sorts all the primitives along an axis (not checking the moving ones) and computes overlapping pairs without saving it. But the memory used to save these primitives is created just once, the first time we add CollisionModels.
Preliminary phase
Before starting the broad phase, two steps are therefore required before the brute force detection starts:
- all present collision models in the scene must be listed. This is done in the function
void PipelineImpl::computeCollisionDetection()with: - from the collision, Axis-Aligned-Bounding-Box (AABB, i.e. CubeModel) will be computed without needing a deep bounding tree (depth level = 1). This is done by each CollisionModel in the scene in the function:
Broad phase
It is one of the most used methods in the broad-phase algorithms because it provides an efficient and quick pairs removal (two objects too far one to the other is deleted) and it does not depend on the objects complexity. The sequential algorithm of SAP takes in input the overall objects of the environment and feeds in output a collided objects pairs list. The algorithm is divided in two principal parts:
- the first one is in charge of the bounding volume update of each active virtual objects. In SOFA, these bounding volume are defined in DSAPBoxes which are simple bounding boxes. Each DSAPBox contains a Cube which contains only one final CollisionElement and pointers to min and max EndPoints.
- the second part is in charge of the detection of overlapping between objects. To do that a projection of higher and upper bounds on the three axis of coordinates (x, y and z) of each AABBs is made.
Only the pairs of objects whose projected bounding volumes overlap on all axes will be saved in the set of active boxes to be considered for the narrow phase. We can notice two related but different concepts on the way the SAP operates internally: the DirectSAP starts from scratch each time even though internal structures could be updated as performed in the IncrSAP.
Narrow phase
The narrow phase browses all boxes considered as active by the broad phase. From this information, it is possible to recover the finest CollisionModel (which is not a CubeModel) corresponding to each box. An intersection check will then be done between these pairs. This check also depends on the intersection method used. This last phase returns the DetectionOutput vector containing elements of CollisionModels in collision and the contact points on the surface of each model.